SKIN CANCERS
One of the most commonly occurring types of cancer in the United States, skin cancer affects approximately 3.3 million people each year. Reducing your exposure to UV rays is one of the best ways of preventing many skin cancers from developing—in fact, exposure to UV rays results in the formation of almost 90% of all melanomas.
What Is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in the United States. It occurs as a result of cells in your body growing out of control—in this case, it is skin cells that rapidly grow and form growths that can be benign or malignant in nature.
According to the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the two most regularly occurring types of skin cancer. Known as nonmelanoma skin cancers, they begin in the squamous and basal cell layers of your skin’s outer surface, known as the epidermis.
Melanoma, the other type of skin cancer, begins in the melanocytes. Despite being much less common than basal cell cancer and squamous cell cancer, melanomas are more severe due to their ability to metastasize and spread to other parts of the body. Melanoma currently accounts for approximately 8,700 deaths each year.
What Are Other Common Skin Conditions?
The skin is the body’s largest organ, and it’s also prone to diseases. The skin is at the forefront of your body’s defense system and, in many cases, your body’s first defense against invaders. Here are a few of the most common conditions that impact the skin:
Many of these problems are preventable or treatable as long as you properly care for your skin.
What Are the Causes
of Skin Cancer?
The most common reason why skin cancer occurs is exposure to UV radiation from the sun or artificial sources such as tanning beds. Avoiding getting sunburned can significantly decrease your risk of melanoma.
However, other risk factors may make you more predisposed to developing skin cancer. These can include:
- Genetics
- Fair skin, red or blonde hair, and light eyes
- Moles
- Exposure to chemicals like arsenic
- Gender: men, in general, are more likely to develop skin cancer than women
- Age
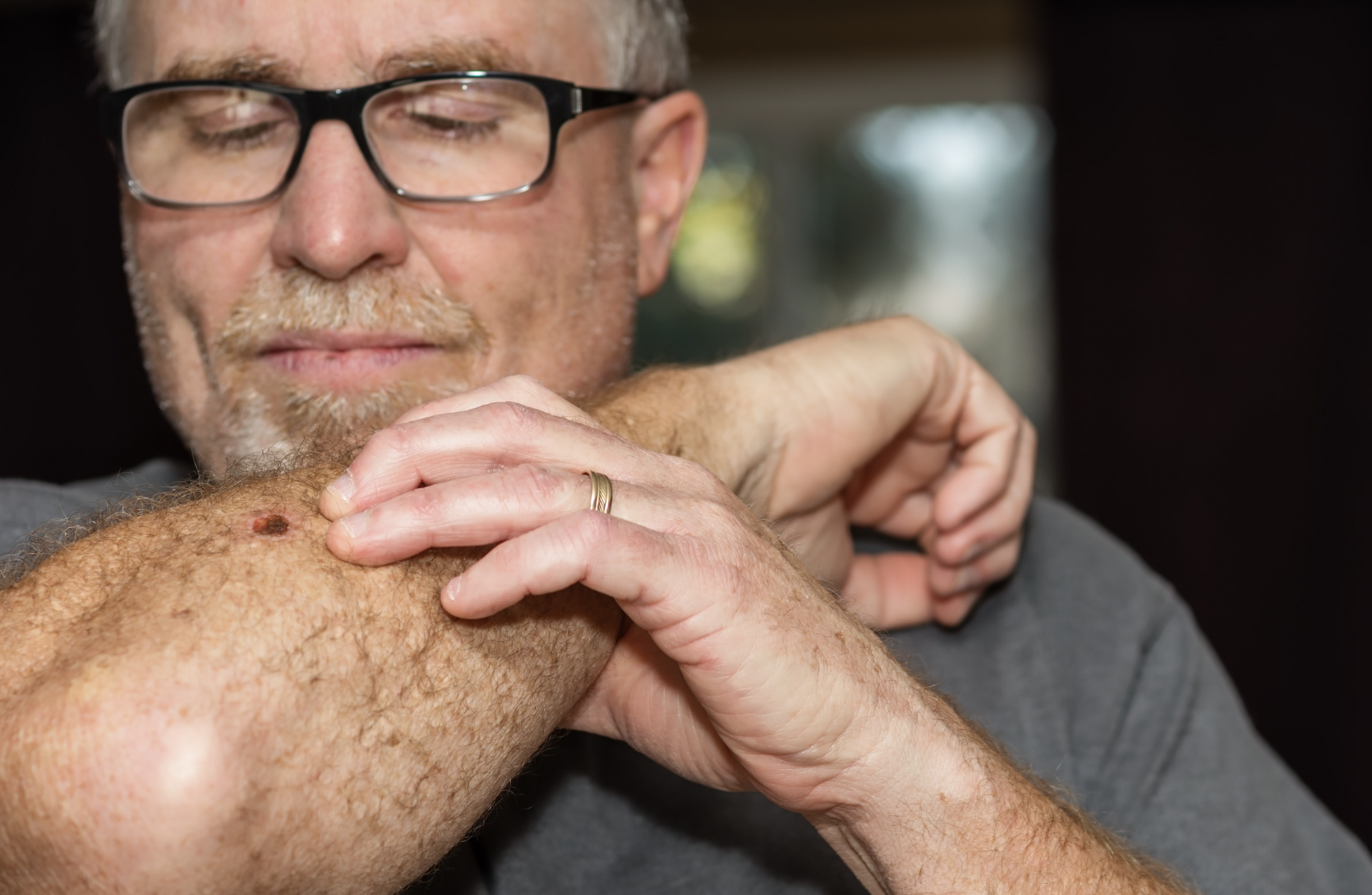
How Are the Symptoms of Skin Cancer?
Skin cancers start as changes to your skin, including the development of new growths, changes to existing moles, or lesions that do not heal.
The ABCDEs are an excellent way to watch out for the symptoms of skin cancer during a self-exam:
- Asymmetrical: Does the growth have an irregular shape
- Border: Does it have a jagged border
- Color: Does it have multiple shades in the bump
- Diameter: Is the mole larger than the size of a pea
- Evolving: Has it grown or changed in appearance recently?
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed?
Any new, unusual, changing, or symptomatic growth should prompt a visit to your dermatologist. If you have risk factors (personal or family history of skin cancers, transplant recipient, significant sun exposure or tanning bed use in the past, etc), scheduling regular appointments with your dermatologist can help with accurate and timely diagnosis and treatment of skin cancers.
Most skin problems manifest physically and are evident by the appearance of your skin. These conditions manifest with physical signs such as redness, itchiness, pain, discomfort, or welts on the surface of the skin. However, because many skin conditions look very similar, there are several tests that your dermatologist will conduct for a conclusive diagnosis.
Patch Testing
Patch testing is used to diagnose allergies by applying a patch of material to a small section of your skin. If there’s a reaction after some time, your doctor can diagnose the allergy.
Skin Biopsy
Skin biopsies are the most common and effective way to diagnose skin cancer. A small piece of skin is cut off and taken for testing to determine whether or not cancer is present.
Culture
Cultures are tests done to determine what type of infection is inflicting your skin. The test is performed similarly to a biopsy–the sample of the infected area is removed and tested.
At your visit, your dermatologist will evaluate your skin and any lesions or growths of concern. A skin biopsy (a procedure that removes a small sample of the skin) is usually done to confirm a definitive diagnosis. Once the diagnosis has been confirmed, your dermatologist will discuss treatment options.
Treatment for Skin Cancer is Safe When Performed by a Board-Certified Dermatologist
For skin cancers that are caught early, treatment by your dermatologist can be effective and prevent them from developing early. Treatment will depend on the:
- Type of skin cancer
- Stage of skin cancer
- Size of the tumor and where it is on the body
your overall health
Typical forms of treatment for skin cancer include:
Simple excision surgery
This procedure involves removing the tumor and surrounding tissue from the skin.
Curettage and electrodesiccation
Commonly known as electrosurgery, this procedure involves using a curette to cut the tumor from the skin. An electronic needle is then used to kill the cancer cells that remain around the wound.
Cryosurgery
Freezing and destroying the cancer cells with the use of liquid nitrogen.
Radiation therapy
Best used to treat nonmelanoma skin cancers, this procedure uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells and prevent future growth.
How to Keep Your Skin Healthy
The best way to prevent the problems mentioned here is by taking protective measures to keep your skin safe. Here are some of the best tips and tricks for keeping your skin healthy and free of problems.
Keep your skin clean by washing your face twice per day and applying moisturizer and toner when necessary. Always use sunblock or sunscreen when you’re planning to spend time in the sun for any length of time. A quick tan is never worth the risk of developing skin cancer or a similar sun-related condition.
It’s good to see a dermatologist annually or as often as needed. Dermatologists are skin specialists that can properly diagnose existing skin conditions and educate you about the best ways to keep your skin healthy.
Pay close attention to your skin. Moles, sun spots, rashes, and other unexpected markings can mean nothing or indicate a more severe problem. You can stay on top of these things before they progress by checking yourself regularly.
If you notice any changes to your skin, reach out to your dermatologist as soon as possible.
Thousands of Bronxites Trust Dermatology and Surgery Associates
Dermatology & Plastic Surgery Under One Roof
Learn More About Our
Dermatology Services
Learn More About Our
